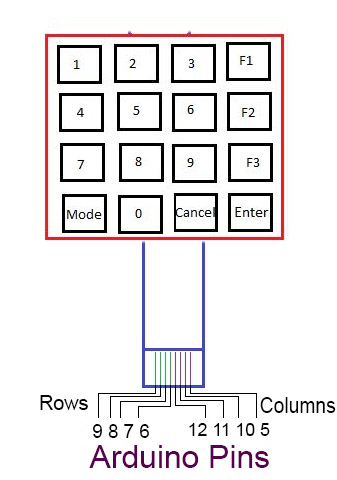
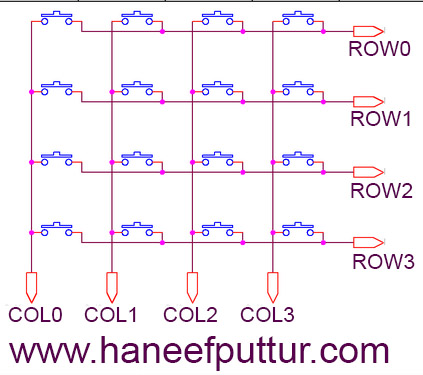
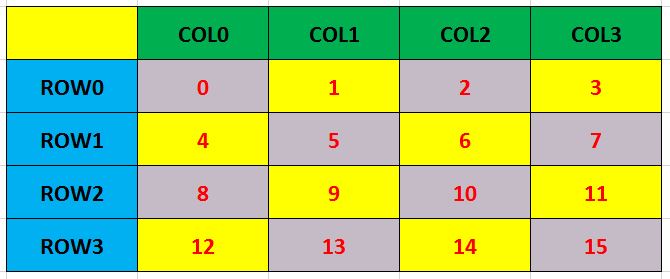
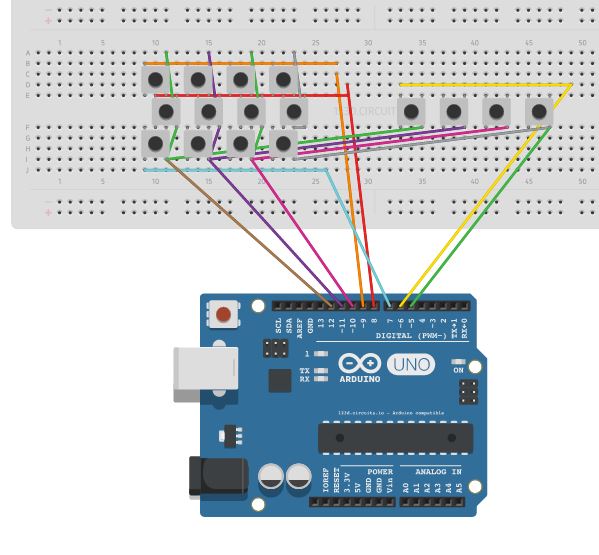
- This is a simple KeyPad Made by Push Buttons , can be extended to any functionalities.
- These buttons can be placed in different places in robotic applications.
- This design does not need any library and also can be expandable to more buttons.
- This design Does not need any Resistors and also does not use any libraries
Parts Required:
- 16 Push Button Switches
- Arduino uno
Connection
- Row Pin Row0 -> Pin 9 of Arduino
- Row Pin Row1 -> Pin 8 of Arduino
- Row Pin Row2 -> Pin 7 of Arduino
- Row Pin Row2 -> Pin 6 of Arduino
- Col Pin Col0 -> Pin 12 of Arduino
- Col Pin Col1 -> Pin 11 of Arduino
- Col Pin Col2 -> Pin 10 of Arduino
- Col Pin Col3 -> Pin 5 of Arduino
Trick is to Use
Find index of any pressed button and assign it
Breadboard Connection
Schematic
PCB
Sketch / Code
//Code by haneefputtur.com
//Using Push Buttons to create 4 X 4 Switch matrix. Can be extended to more buttons
//Data will be displayed in serial monitor for testing project
byte h=0,v=0; //variables used in for loops
const unsigned long period=50; //little period used to prevent error
unsigned long kdelay=0; // variable used in non-blocking delay
const byte rows=4; //number of rows of keypad
const byte columns=4; //number of columnss of keypad
const byte Output[rows]={9,8,7,6}; //array of pins used as output for rows of keypad
const byte Input[columns]={12,11,10,5}; //array of pins used as input for columnss of keypad
byte keypad() // function used to detect which button is used
{
static bool no_press_flag=0; //static flag used to ensure no button is pressed
for(byte x=0;x<columns;x++) // for loop used to read all inputs of keypad to ensure no button is pressed
{
if (digitalRead(Input[x])==HIGH); //read evry input if high continue else break;
else
break;
if(x==(columns-1)) //if no button is pressed
{
no_press_flag=1;
h=0;
v=0;
}
}
if(no_press_flag==1) //if no button is pressed
{
for(byte r=0;r<rows;r++) //for loop used to make all output as low
digitalWrite(Output[r],LOW);
for(h=0;h<columns;h++) // for loop to check if one of inputs is low
{
if(digitalRead(Input[h])==HIGH) //if specific input is remain high (no press on it) continue
continue;
else //if one of inputs is low
{
for (v=0;v<rows;v++) //for loop used to specify the number of row
{
digitalWrite(Output[v],HIGH); //make specified output as HIGH
if(digitalRead(Input[h])==HIGH) //if the input that selected from first sor loop is change to high
{
no_press_flag=0; //reset the no press flag;
for(byte w=0;w<rows;w++) // make all outputs as low
digitalWrite(Output[w],LOW);
return v*4+h; //return number of button
}
}
}
}
}
return 50;
}
void setup()
{
for(byte i=0;i<rows;i++) //for loop used to make pin mode of outputs as output
{
pinMode(Output[i],OUTPUT);
}
for(byte s=0;s<columns;s++) //for loop used to makk pin mode of inputs as inputpullup { pinMode(Input[s],INPUT_PULLUP); } Serial.begin(9600); //to use serial monitor we set the buad rate } void loop() { if(millis()-kdelay>period) //used to make non-blocking delay
{
kdelay=millis(); //capture time from millis function
switch (keypad()) //switch used to specify which button
{
case 0:
Serial.println(1);
break;
case 1:
Serial.println(2);
break;
case 2:
Serial.println(3);
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("F1");
break;
case 4:
Serial.println(4);
break;
case 5:
Serial.println(5);
break;
case 6:
Serial.println(6);
break;
case 7:
Serial.println("F2");
break;
case 8:
Serial.println(7);
break;
case 9:
Serial.println(8);
break;
case 10:
Serial.println(9);
break;
case 11:
Serial.println("F3");
break;
case 12:
Serial.println("Mode");
break;
case 13:
Serial.println(0);
break;
case 14:
Serial.println("Cancel");
break;
case 15:
Serial.println("Enter");
break;
default:
;
}
}
}
To see the simulation visit my lab at : https://123d.circuits.io/circuits/1741944
and click start Simulation.
You can press buttons and see the outputs at Serial Monitor